智能化农业装备学报(中英文) ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (1): 1-14.DOI: 10.12398/j.issn.2096-7217.2025.01.001
• • 下一篇
吴擎1,2( ), 韦润轩1, 周乐1, 杨浩1, 刘婉茹1, 徐红梅1,2(
), 韦润轩1, 周乐1, 杨浩1, 刘婉茹1, 徐红梅1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-14
修回日期:2024-08-19
出版日期:2025-02-15
发布日期:2025-02-15
通讯作者:
徐红梅
作者简介:吴擎,女,1988年生,湖北孝感人,博士,副教授;研究方向为深度学习及其应用。E-mail: wuqing@mail.hzau.edu.cn
基金资助:
WU Qing1,2( ), WEI Runxuan1, ZHOU Le1, YANG Hao1, LIU Wanru1, XU Hongmei1,2(
), WEI Runxuan1, ZHOU Le1, YANG Hao1, LIU Wanru1, XU Hongmei1,2( )
)
Received:2024-05-14
Revised:2024-08-19
Online:2025-02-15
Published:2025-02-15
Contact:
XU Hongmei
About author:WU Qing,E-mail: wuqing@mail.hzau.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
茶芽分类识别是名优茶生产中十分重要的环节。针对目前茶芽识别算法模型尺寸大、计算量大且无法区分采摘形态等问题,本研究以YOLOv5s为基线模型,提出了一种改进的鲜茶叶识别模型(YOLOv5s-SPCS)。首先,收集实验室环境和自然环境下的鲜茶叶图像制作鲜茶叶数据集。其次,基于ShuffleNetV2思想构建Shuffle Block模块替换主干网络中的卷积模块,在减少模型参数量和计算量的同时提高特征提取速度。然后,在颈部网络引入部分卷积结构PConv和无参数注意力机制SimAM构建C3-PCS模块替换原C3结构,减少模型计算冗余和内存访问,提高识别精度。最后,采用SIoU作为边界框损失函数,提高预测框收敛速度和收敛精度。试验结果表明,YOLOv5s-SPCS模型参数量、计算量和权重文件大小分别为YOLOv5s模型的14%、14%和16%,对鲜茶叶识别准确率为81.8%、平均精度均值为82.4%,相较于原始模型,准确率提升了2.7个百分点,平均精度均值保持不变。此外,改进后的YOLOv5s-SPCS模型整体性能优于当前常用的Faster R-CNN、SSD、YOLOv3、YOLOv4等目标检测模型。本研究可为鲜茶叶识别分类及后续移动端部署提供有效的技术支持。
中图分类号:
吴擎, 韦润轩, 周乐, 杨浩, 刘婉茹, 徐红梅. 基于改进YOLOv5s的轻量化鲜茶叶识别方法[J]. 智能化农业装备学报(中英文), 2025, 6(1): 1-14.
WU Qing, WEI Runxuan, ZHOU Le, YANG Hao, LIU Wanru, XU Hongmei. Lightweight fresh tea leaf recognition method based on improved YOLOv5s[J]. Journal of Intelligent Agricultural Mechanization, 2025, 6(1): 1-14.
| 模型 | 深度 | 宽度 | 参数量 /×106 M | 浮点运算量 FLOPs/G |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5n | 0.33 | 0.25 | 1.76 | 4.1 |
| YOLOv5s | 0.33 | 0.50 | 7.02 | 15.8 |
| YOLOv5m | 0.67 | 0.75 | 20.86 | 47.9 |
| YOLOv5l | 1.00 | 1.00 | 46.15 | 108.3 |
| YOLOv5x | 1.33 | 1.25 | 86.23 | 204.7 |
表1 YOLOv5系列参数对比
Table 1 YOLOv5 series parameter comparison
| 模型 | 深度 | 宽度 | 参数量 /×106 M | 浮点运算量 FLOPs/G |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5n | 0.33 | 0.25 | 1.76 | 4.1 |
| YOLOv5s | 0.33 | 0.50 | 7.02 | 15.8 |
| YOLOv5m | 0.67 | 0.75 | 20.86 | 47.9 |
| YOLOv5l | 1.00 | 1.00 | 46.15 | 108.3 |
| YOLOv5x | 1.33 | 1.25 | 86.23 | 204.7 |

图6 YOLOv5s网络结构注:Conv2D为常规卷积操作;BN为批量归一化操作;SiLU为激活函数;Bottleneck为残差结构;Concat为张量拼接操作;MaxPool为最大池化操作;SPPF为空间金字塔池化结构;Upsample为上采样操作;CBS模块由Conv2D、BN和SiLU组成;CSP1_X为包含X个Bottleneck的卷积结构;CSP2_X为包含2X个CBS的卷积结构。
Figure 6 The network structure of YOLOv5s

图7 YOLOv5s-SPCS网络结构注:ReLU为激活函数;PConv为部分卷积操作;SimAM为无参数注意力机制模块;PCS Bottleneck为引入PConv和SimAM后的残差结构;C3-PCS为新的C3模块;CBRM模块由Conv、BN、ReLU和MaxPool组成;PCBS模块由PConv、BN和SiLU组成;Shuffle Block是基本的ShuffleNet模块。
Figure 7 The network structure of YOLOv5s-SPCS
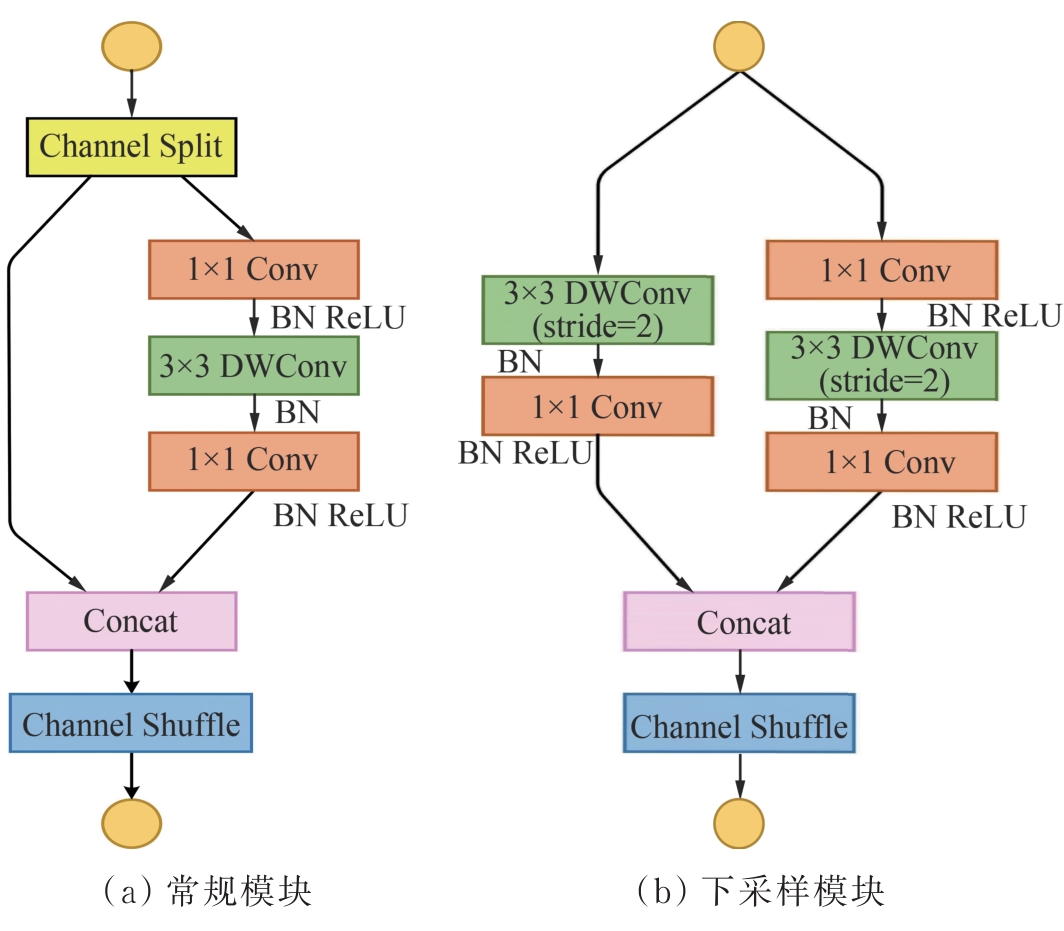
图8 Shuffle Block轻量化模块结构注:Channel Split为通道拆分操作;Conv为常规卷积操作;DWConv(depthwise convolution)为深度可分离卷积;Concat为张量拼接;Channel Shuffle为通道重排。
Figure 8 Structure of Shuffle Block lightweight module
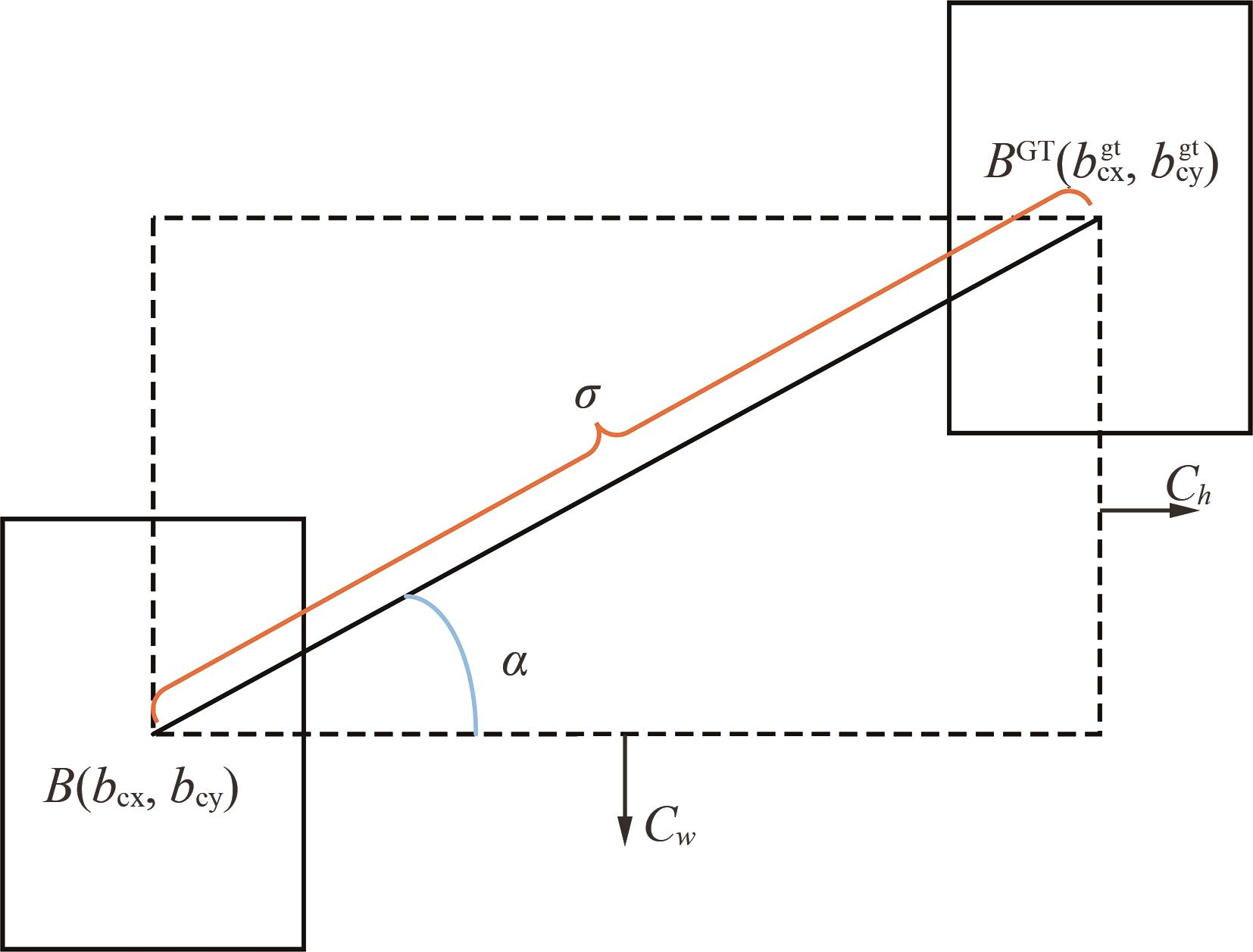
图11 SIoU参数示意图注:B和BGT分别为预测框中心点和真实框中心点,(bcx,bcy)和(bcxgt,bcygt)分别是B和BGT的坐标。Cw 和Ch 分别是B和BGT横纵坐标的差值,α为B和BGT连线与水平轴夹角,σ为B和BGT连线长度。
Figure 11 SIoU parameters schematic diagram
Shuffle Block | PConv | SimAM | SIoU | 精确度 P/% | 召回率 R/% | 平均精度均值 mAP/% | 参数量 Params/×106 M | 浮点运算量 FLOPs/G | 权重文件大小 /MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| × | × | × | × | 79.1 | 72.1 | 82.4 | 7.02 | 15.8 | 13.67 |
| √ | × | × | × | 78.2 | 69.1 | 80.4 | 0.85 | 1.8 | 1.85 |
| × | √ | × | × | 82.3 | 72.3 | 82.1 | 7.20 | 16 | 14.03 |
| × | × | √ | × | 82.1 | 72.7 | 82.5 | 7.29 | 17.2 | 14.20 |
| √ | √ | × | × | 79.5 | 68.2 | 81.4 | 0.89 | 1.9 | 1.95 |
| × | √ | √ | × | 80.9 | 73.1 | 82.6 | 7.48 | 17.4 | 14.56 |
| √ | × | √ | × | 78.1 | 70.3 | 80.9 | 0.91 | 2.2 | 1.99 |
| √ | √ | √ | × | 81.8 | 71.9 | 81.2 | 0.96 | 2.2 | 2.09 |
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 81.8 | 72.5 | 82.4 | 0.96 | 2.2 | 2.09 |
表2 网络消融试验
Table 2 Network ablationtest
Shuffle Block | PConv | SimAM | SIoU | 精确度 P/% | 召回率 R/% | 平均精度均值 mAP/% | 参数量 Params/×106 M | 浮点运算量 FLOPs/G | 权重文件大小 /MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| × | × | × | × | 79.1 | 72.1 | 82.4 | 7.02 | 15.8 | 13.67 |
| √ | × | × | × | 78.2 | 69.1 | 80.4 | 0.85 | 1.8 | 1.85 |
| × | √ | × | × | 82.3 | 72.3 | 82.1 | 7.20 | 16 | 14.03 |
| × | × | √ | × | 82.1 | 72.7 | 82.5 | 7.29 | 17.2 | 14.20 |
| √ | √ | × | × | 79.5 | 68.2 | 81.4 | 0.89 | 1.9 | 1.95 |
| × | √ | √ | × | 80.9 | 73.1 | 82.6 | 7.48 | 17.4 | 14.56 |
| √ | × | √ | × | 78.1 | 70.3 | 80.9 | 0.91 | 2.2 | 1.99 |
| √ | √ | √ | × | 81.8 | 71.9 | 81.2 | 0.96 | 2.2 | 2.09 |
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 81.8 | 72.5 | 82.4 | 0.96 | 2.2 | 2.09 |
| 类别 | 精确率 P/% | 召回率 R/% | 平均精度 均值 mAP/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 全类别 | 81.8 | 72.5 | 82.4 |
| 一芽一叶 | 79.5 | 75.5 | 85.3 |
| 一芽二叶 | 86.5 | 79.1 | 89.4 |
| 单芽 | 79.9 | 61.2 | 72.1 |
表3 YOLOv5s-SPCS模型三分类目标检测性能
Table 3 Three-classification target detection performance of YOLOv5s-SPCS
| 类别 | 精确率 P/% | 召回率 R/% | 平均精度 均值 mAP/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 全类别 | 81.8 | 72.5 | 82.4 |
| 一芽一叶 | 79.5 | 75.5 | 85.3 |
| 一芽二叶 | 86.5 | 79.1 | 89.4 |
| 单芽 | 79.9 | 61.2 | 72.1 |
| 主干网络 | 平均精度均值 mAP/% | 参数量 Params/×106 M | 浮点运算量 FLOPs/G | 模型大小 /MB | 帧率 FPS/(帧·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MobileNetV3 | 81.9 | 1.38 | 2.3 | 2.92 | 52.68 |
| GhostNet | 83.1 | 5.08 | 10.6 | 10.03 | 38.33 |
| ShuffleNetV2 | 82.4 | 0.96 | 2.2 | 2.09 | 67.87 |
表4 不同轻量化方法对比试验
Table 4 Comparison experimental of different lightweight approaches
| 主干网络 | 平均精度均值 mAP/% | 参数量 Params/×106 M | 浮点运算量 FLOPs/G | 模型大小 /MB | 帧率 FPS/(帧·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MobileNetV3 | 81.9 | 1.38 | 2.3 | 2.92 | 52.68 |
| GhostNet | 83.1 | 5.08 | 10.6 | 10.03 | 38.33 |
| ShuffleNetV2 | 82.4 | 0.96 | 2.2 | 2.09 | 67.87 |
| 损失函数 | 平均精度均值 mAP/% | 检测时间 /ms | 帧率 FPS/(帧·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GIoU | 81.7 | 15.2 | 65.42 |
| DIoU | 82.3 | 15.1 | 66.30 |
| CIoU | 81.5 | 15.2 | 66.21 |
| EIoU | 82.4 | 14.8 | 67.32 |
| SIoU | 82.4 | 14.7 | 67.87 |
表5 不同边界框损失函数对比试验
Table 5 Comparison experimental using different IoU
| 损失函数 | 平均精度均值 mAP/% | 检测时间 /ms | 帧率 FPS/(帧·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GIoU | 81.7 | 15.2 | 65.42 |
| DIoU | 82.3 | 15.1 | 66.30 |
| CIoU | 81.5 | 15.2 | 66.21 |
| EIoU | 82.4 | 14.8 | 67.32 |
| SIoU | 82.4 | 14.7 | 67.87 |
| 模型 | 精确率 P/% | 平均精度均值 mAP/% | 参数量 Params/×106 M | 浮点运算量 FLOPs/G | 模型大小 /MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | - | 72.2 | 136.73 | 369.8 | 521.60 |
| SSD-300 | - | 63.7 | 23.88 | 61.0 | 91.63 |
| YOLOv3 | 80.9 | 82.1 | 61.51 | 154.6 | 117.73 |
| YOLOv3-tiny | 81.3 | 79.4 | 8.67 | 12.9 | 16.63 |
| YOLOv4 | 80.2 | 82.5 | 60.40 | 130.7 | 115.80 |
| YOLOv4-tiny | 79.6 | 81.6 | 3.07 | 6.4 | 5.96 |
| YOLOv5s | 79.1 | 82.4 | 7.02 | 15.8 | 13.67 |
| YOLOv7 | 83.3 | 81.9 | 37.21 | 105.1 | 71.32 |
| YOLOv5s-SPCS | 81.8 | 82.4 | 0.96 | 2.2 | 2.09 |
表6 不同检测模型对比试验
Table 6 Comparison experimental of different detection models
| 模型 | 精确率 P/% | 平均精度均值 mAP/% | 参数量 Params/×106 M | 浮点运算量 FLOPs/G | 模型大小 /MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | - | 72.2 | 136.73 | 369.8 | 521.60 |
| SSD-300 | - | 63.7 | 23.88 | 61.0 | 91.63 |
| YOLOv3 | 80.9 | 82.1 | 61.51 | 154.6 | 117.73 |
| YOLOv3-tiny | 81.3 | 79.4 | 8.67 | 12.9 | 16.63 |
| YOLOv4 | 80.2 | 82.5 | 60.40 | 130.7 | 115.80 |
| YOLOv4-tiny | 79.6 | 81.6 | 3.07 | 6.4 | 5.96 |
| YOLOv5s | 79.1 | 82.4 | 7.02 | 15.8 | 13.67 |
| YOLOv7 | 83.3 | 81.9 | 37.21 | 105.1 | 71.32 |
| YOLOv5s-SPCS | 81.8 | 82.4 | 0.96 | 2.2 | 2.09 |
| 1 | 梅宇, 张朔. 2022年中国茶叶生产与内销形势分析[J]. 中国茶叶, 2023, 45(4): 25-30. |
| MEI Yu, ZHANG Shuo. Analysis of China's tea production and domestic sales in 2022 [J]. China Tea, 2023, 45(4): 25-30. | |
| 2 | 高震宇, 王安, 刘勇, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的鲜茶叶智能分选系统研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2017, 48(7): 53-58. |
| GAO Zhenyu, WANG An, LIU Yong, et al. Intelligent fresh-tea-leaves sorting system research based on convolution neural network [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(7): 53-58. | |
| 3 | 韩余, 宋志禹, 陈巧敏. 4CJ-1200F智能采茶机设计与试验[J]. 智能化农业装备学报(中英文), 2022, 3(1): 1-6. |
| HAN Yu, SONG Zhiyu, CHEN Qiaomin. Design and experiment of 4CJ-1200F intelligent tea plucking machine [J]. Journal of Intelligent Agricultural Mechanization, 2022, 3(1): 1-6. | |
| 4 | 胡程喜, 谭立新, 王文胤, 等. 基于改进DeepLabV3+的轻量化茶叶嫩芽采摘点识别模型[J]. 智慧农业(中英文), 2024, 6(5): 119-127. |
| HU Chengxi, TAN Lixin, WANG Wenyin, et al. Lightweight tea shoot picking point recognition model based on improved DeepLabV3+ [J]. Smart Agriculture, 2024, 6(5): 119-127. | |
| 5 | 张兰兰, 董迹芬, 唐萌, 等. 名优茶机采鲜叶分级技术研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2012, 38(5): 593-598. |
| ZHANG Lanlan, DONG Jifen, TANG Meng, et al. Classification technology of machine-plucking high quality tea [J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences), 2012, 38(5): 593-598. | |
| 6 | 唐小林, 李文萃, 范起业. 机采茶鲜叶分类分级技术及相关设备研究进展[J]. 中国茶叶加工, 2015(2): 5-8. |
| TANG Xiaolin, LI Wencui, FAN Qiye. Research on the classification technology and the grading equipment of machine-plucking fresh leaves [J]. China Tea Processing, 2015(2): 5-8. | |
| 7 | 孙道宗, 张振宇, 陈俊聪, 等. 一种基于深度学习的端到端生菜无损鲜重估测模型的建立[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2024, 47(6): 1212-1220. |
| SUN Daozong, ZHANG Zhenyu, CHEN Juncong, et al . A model for end-to-end non-destructive fresh weight estimation of lettuce based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2024, 47(6): 1212-1220. | |
| 8 | 黄印. 基于机器学习的鲜茶叶分类研究[D]. 武汉: 中南民族大学, 2021. |
| HUANG Yin. Research on classification of fresh tea based on machine learning [D]. Wuhan: South-Central Minzu University, 2021. | |
| 9 | 范婷婷. 基于高光谱成像技术的茶叶无损检测方法研究[D]. 天津: 河北工业大学, 2021. |
| FAN Tingting. Research on nondestructive detection method of tea based on hyperspectral imaging technology [D]. Tianjin: Hebei University of Technology, 2021. | |
| 10 | 陈忠辉. 基于计算机视觉的茶叶嫩芽识别方法研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2022. |
| CHEN Zhonghui. Research on the method of tea sprout recognition based on computer vision [D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2022. | |
| 11 | 邢洁洁, 谢定进, 杨然兵, 等. 基于YOLOv5s的农田垃圾轻量化检测方法[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(19): 153-161. |
| XING Jiejie, XIE Dingjin, YANG Ranbing, et al. Lightweight detection method for farmland waste based on YOLOv5s [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(19): 153-161. | |
| 12 | SHANG Y Y, XU X S, JIAO Y T, et al. Using lightweight deep learning algorithm for real-time detection of apple flowers in natural environments [J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2023, 207: 107765. |
| 13 | 黄家才, 唐安, 陈光明, 等. 基于Compact-YOLO v4的茶叶嫩芽移动端识别方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2023, 54(3): 282-290. |
| HUANG Jiacai, TANG An, CHEN Guangming, et al. Mobile recognition solution of tea buds based on Compact-YOLO v4 algorithm [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2023, 54(3): 282-290. | |
| 14 | ZHU L X, ZHANG Z H, LIN G C, et al. Detection and localization of tea bud based on improved YOLOv5s and 3D point cloud processing [J]. Agronomy, 2023, 13(9): 2412. |
| 15 | GUI Z Y, CHEN J N, LI Y, et al. A lightweight tea bud detection model based on Yolov5 [J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2023, 205: 107636. |
| 16 | 王梦妮, 顾寄南, 王化佳, 等. 基于改进YOLOv5s模型的茶叶嫩芽识别方法[J]. 农业工程学报, 2023, 39(12): 150-157. |
| WANG Mengni, GU Jinan, WANG Huajia, et al. Method for identifying tea buds based on improved YOLOv5s model [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2023, 39(12): 150-157. | |
| 17 | 白强, 高荣华, 赵春江, 等. 基于改进YOLOV5s网络的奶牛多尺度行为识别方法[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(12): 163-172. |
| BAI Qiang, GAO Ronghua, ZHAO Chunjiang, et al. Multi-scale behavior recognition method for dairy cows based on improved YOLOV5s network [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(12): 163-172. | |
| 18 | WOLPERT D H, MACREADY W G. No free lunch theorems for optimization [J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 1997, 1(1): 67-82. |
| 19 | LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection [C]// 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway, New Jersey: IEEE, 2017: 936-944. |
| 20 | LIU S, QI L, QIN H F, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation [C]// 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway, New Jersey: IEEE, 2018: 8759-8768. |
| 21 | MA N N, ZHANG X Y, ZHENG H T, et al. ShufflenetV2: Practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design [C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). 2018: 116-131. |
| 22 | ZHANG X Y, ZHOU X Y, LIN M X, et al. Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2018: 6848-6856. |
| 23 | CHEN J R, KAO S H, HE H, et al. Run, Don't walk: Chasing higher FLOPS for faster neural networks [C]// Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2023: 12021-12031. |
| 24 | YANG L X, ZHANG R Y, LI L D, et al. SimAM: A simple, parameter-free attention module for convolutional neural networks [C]// International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2021: 11863-11874. |
| 25 | GEVORGYAN Z. SIoU loss: More powerful learning for bounding box regression [J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: , 2022. |
| 26 | HOWARD A, SANDLER M, CHEN B, et al. Searching for MobileNetV3 [C]// 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Piscataway, New Jersey: IEEE, 2019: 1314-1324. |
| 27 | HAN K, WANG Y H, TIAN Q, et al. GhostNet: More features from cheap operations [C]// 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway, New Jersey: IEEE, 2020: 1577-1586. |
| 28 | REZATOFIGHI H, TSOI N, GWAK J, et al. Generalized intersection over union: A metric and a loss for bounding box regression [C]// 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway, New Jersey: IEEE, 2019: 658-666. |
| 29 | ZHENG Z H, WANG P, REN D W, et al. Enhancing geometric factors in model learning and inference for object detection and instance segmentation [J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(8): 8574-8586. |
| 30 | ZHANG Y F, REN W Q, ZHANG Z, et al. Focal and efficient IoU loss for accurate bounding box regression [J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 506: 146-157. |
| 31 | REN S Q, HE K M, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 39(6): 1137-1149. |
| 32 | 周华茂, 王婧, 殷华, 等. 基于改进 Mask R-CNN 模型的秀珍菇表型参数自动测量方法[J]. 智慧农业(中英文), 2023, 5(4): 117-126. |
| ZHOU Huamao, WANG Jing, YIN Hua, et al. Phenotype analysis of Pleurotus geesteranus based on improved Mask R-CNN [J]. Smart Agriculture, 2023, 5(4): 117-126. | |
| 33 | 郭小燕,于帅卿 . 一种轻量级 YOLOv5S 农作物虫害目标检测模型[J]. 南京农业大学学报,2024,47(5): 1009-1018. |
| GUO Xiaoyan, YU Shuaiqing . A lightweight YOLOv5S crop pest target detection model[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2024, 47(5): 1009-1018. | |
| 34 | REDMON J, FARHADI A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement [J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: , 2018. |
| 35 | BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection [J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: , 2020. |
| 36 | WANG C Y, BOCHKOVSKIY A, LIAO H Y M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors [C]// 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway, New Jersey: IEEE, 2023: 7464-7475. |
| 37 | SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization [C]// Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2017: 618-626. |
| [1] | 王元红, 杨志明, 王琪, 卢劲竹, 高俊锋. 基于YOLOv5s-SPD的茶芽识别方法及识别系统光源设计与试验[J]. 智能化农业装备学报(中英文), 2024, 5(3): 33-43. |
| [2] | 高宁, 张安琪, 梅鹤波, 杨兴华, 甘蕾, 孟志军. 土壤墒情监测技术研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 智能化农业装备学报(中英文), 2024, 5(3): 51-62. |
| [3] | 魏堂伟, 张津诚, 王晶, 周庆燕. 基于改进YOLOv7的茶叶嫩芽识别模型研究[J]. 智能化农业装备学报(中英文), 2024, 5(2): 42-50. |
| [4] | 郭文娟, 冯全. 基于类激活映射的可解释性方法在农作物检测识别中的发展现状与趋势[J]. 智能化农业装备学报(中英文), 2023, 4(4): 41-48. |
| [5] | 黄成龙, 张忠福, 卢智浩, 张晓君, 朱龙付, 杨万能. 基于VFNet-Improved和Deep Sort的棉花黄萎病病情分级[J]. 智能化农业装备学报(中英文), 2023, 4(2): 12-21. |
| [6] | 肖张娜, 罗陆锋, 陈明猷, 王金海, 卢清华, 骆少明. 基于改进YOLO-v4的果园环境下葡萄检测[J]. 智能化农业装备学报(中英文), 2023, 4(2): 35-43. |
| [7] | 李搴曦, 孙晓明, 江晗慧, 吴爱茹, 傅隆生, 李瑞. 基于YOLOv4-tiny的设施番茄智能喷药无人车设计与试验[J]. 智能化农业装备学报(中英文), 2023, 4(2): 44-52. |
| [8] | 王红君, 季晓宇, 赵辉, 岳有军. SENet优化的Deeplabv3+淡水鱼体语义分割*[J]. 智能化农业装备学报(中英文), 2021, 2(1): 36-43. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
